unusual powder gas jet (right) from the dark side of Comet 67P. (DLR / ESA)
Usually comets eject gas and dust into space mainly from the areas of its exposed to direct sunlight surface, however Rosetta surprised to Comet 67P / Churyumov -Gerasimenko expelling from its dark side.
This happened in mid-March, when 67P was about 75 kilometers from the imaging system to optical, spectroscopic and infrared remote, called OSIRIS, which is aboard the ship Rosetta . “It’s an extraordinary phenomenon that occurs in the 67P / Churyumov-Gerasimenko. A new powder jet – of currently unknown origin – was suddenly released from the shady side, “he said the German Space Agency (DLR), April 20
..” This is the first time we have been able to observe the moment of birth a new jet of dust, “said Ekkehard Kuhrt comet researcher in charge of the scientific contribution of the Rosetta mission of the European Space Agency ESA and DLR.
Comet 67P / Churyumov-Gerasimenko is getting closer to the sun. Weeks before the images of the curious jet had begun to be much more active.
As the surface has warmed It has been expelling large amounts of gas with dust particles into space, the mission team reported.
But the powder jet observed in March was totally unexpected. “It’s exciting to think about how comets can become active in their shadow sides,” said Jörg Knollenberg, DLR researcher kites. “However, it is quite possible that sunlight falling on areas previously hidden behind mountain ridges. We will have to continue to observe and take measurements before we can arrive at a plausible explanation, “concluded the researcher.
The comet 67P is already wrapped by a comma dust that escapes through the surface around the side of the daylight. This will become more evident in the coming months until its closest approach to the Sun in about August.
“We looked brightness fluctuations along the jet could estimate unexpected dust and particles traveling away from comet at a speed of at least eight meters per second, “said Knollenberg.
The new measurement confirms earlier about the ejection of dust from the comet’s sunlit side.
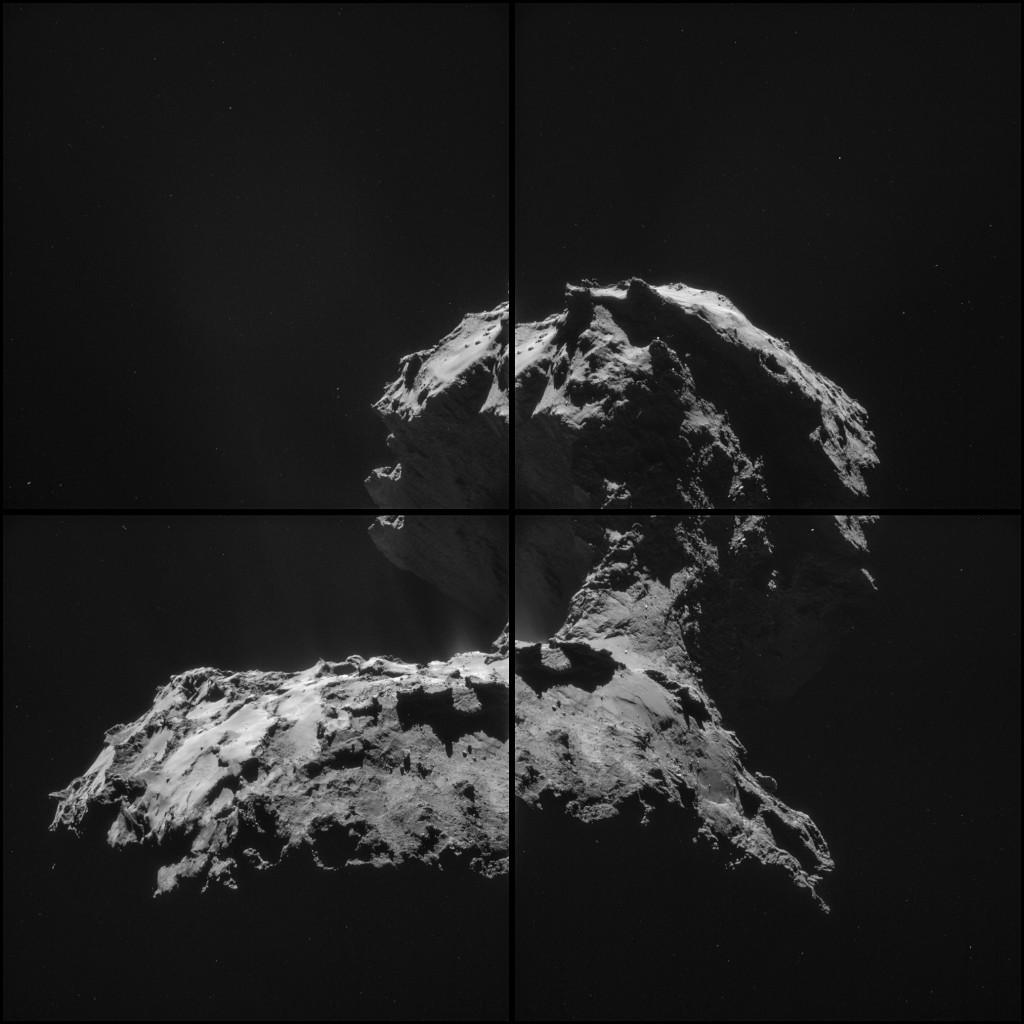

Comet 67P. (ESA)
“These observations help decipher the cometary activity we have been unable to fully understand yet,” said the German agency.
Regional Map of Comet 67P. (ESA / Rosetta / MPS for OSIRIS Team MPS / UPD / LAM / IAA / SSO / INTA / UPM / DASP / IDA)
No comments:
Post a Comment